Linked List
CCI
Remove Dups
Reverse Linked List
Return Kth to Last
Delete Middle Node
Partition
Sum List
Palindrome
Intersection
Loop Detection
Leet Code
Remove Dups
Write code to remove duplicate element from unsorted.
solution
| Time complexity | Space Complexity | |
|---|---|---|
| Using buffer (hash table) | O(n) | O(n) |
| Without buffer | O(n**2) | O(1) |
Using buffer
- Track counts of each elements by using hash table. If it exists, delete it. Time complexity will be O(N).
Without buffer
- we can use a pointer. The pointer goes to the end of the list, and check if the value of pointed node is same as the value of current value.
Code
https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/remove-duplicates-from-a-sorted-linked-list/
Reverse Linked List
Reverse Linked List
['A', 'B', 'C', 'D', 'E' , 'F', 'G']
solution
| Time complexity | Space complexity | |
|---|---|---|
| Iteration | O(n) | O(1) |
Iterate over nodes
Save current node's next next node because the pointer to next next node will be lost by assigning new node to next node.
- For example, current node is 'A', next node is 'B', and next next node is 'C' on first iteration. 'B' has pointer to 'C' but we want to replace it to 'A'. At that point, the pointer to 'C' will be gone so we need to keep node 'C' and Assign node 'B' to the next pointer of node 'C'.
Switch the pointer of current node's next node to current node.
Code
Return Kth to Last
Find the Kth to last element of a singly linked list
'A', 'B', 'C', 'D', 'E' , 'F', 'G'
6 5 4 3 2 1 . 0
solution
| Time | Space | |
|---|---|---|
| Recursion | O(n) | O(n) |
| While loop | O(n) | O(1) |
- Recursion
- Goes to last end node.
- If it goes to end node, return 0 as index
- if index === k, return node
Code
Delete Middle Node
Implement an algorithm to delete a node in the middle.
solution
| Time complexity | Space complexity | |
|---|---|---|
| Two pointer (slow and fast) | O(n) | O(1) |
- Two pointer
- Prepare slow pointer and fast pointer.
- The slow pointer traverses by one node, while The fast pointer traverses by two nodes.
- If fast pointer reaches to the end, slow pointer is at middle.
Code
Partition
Given a linked list and a valuex, partition it such that all nodes less thanx_come before nodes greater than or equal to_x.
You should preserve the original relative order of the nodes in each of the two partitions.
solution
| Time complexity | Space complexity | |
|---|---|---|
| Two Linked List | O(n) | O(n) |
Two Linked List
Code
Sum List
Given two numbers represented by a linked list, where each node contains a single digit. The digits are stored in reverse order. Write a function sum and return the numbers and
Input
Linked List 1: (7 -> 1 -> 6) - 617
Linked List 2: (5 -> 9 -> 2) - 295
Output
(2 -> 1 -> 9) - 912
solution
| Time | Space | |
|---|---|---|
| Recursion | O(n) | O(1) |
- Write a function takes three arguments which are (node1, node2, carryValue)
- Sum node1 value and node2 value and carryValue up
- If the sum of two digits is more than equal 10, then pass 1 as carry value and the second digit is the value of node.
- Recursively call self
- return head
Code
Palindrome
Check if the given Linked List is palindrome.
https://www.programcreek.com/2014/07/leetcode-palindrome-linked-list-java/
solution
| Time | Space | |
|---|---|---|
| Reverse and compare | O(N) | O(1) |
| Iteration | O(N) | O(1) |
| Recrusive | O(N) | O(N) |
Code
Intersection
Given two Linked Lists, determine if the two lists intersect. Return the intersection of node.
- Intersection is defined by Node, not value
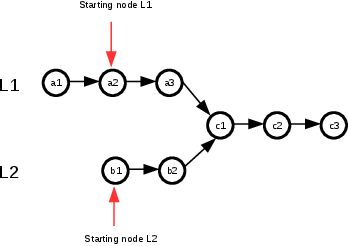
solution
Run though each linked list and check the length
Compare the tails. If they are different, return immediately because there is no intersection.
Set 2 pointers to start
Advance the pointer on the longer Linked List by the difference in lengths
traverse and if it is same
Code
Loop Detection
Find loop inside LinkedList

solution
| Time Complexity | Space Complexity | |
|---|---|---|
| Two pointer | O(N) | O(1) |
- Run though each linked list and check the length
- Compare the tails. If they are different, return immediately because there is no intersection.
- Set 2 pointers to start
- Advance the pointer on the longer Linked List by the difference in lengths
- traverse and if it is same