Data Structure
Array
Linked List
Stack
Queue
Tree
Trie
Heap
Graph
Hash Table
Set
Array
Linked List
When to use
- You need constant-time insertions/deletions from the list (such as in real-time computing where time predictability is absolutely critical)
You don't know how many items will be in the list. With arrays, you may need to re-declare and copy memory if the array grows too big
You don't need random access to any elements
You want to be able to insert items in the middle of the list (such as a priority queue)
https://stackoverflow.com/questions/393556/when-to-use-a-linked-list-over-an-array-array-list
Example
- Low Level Memory Management
Web browsers history
File allocation table
https://www.cs.princeton.edu/courses/archive/fall13/cos217/lectures/21DynamicMemory2.pdf
Type
Singly Linked List
Doubly Linked List
Circular Linked List
Skip List
Spray List
Singly Linked List
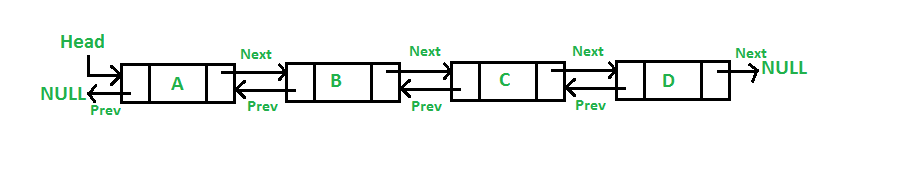
Doubly Linked List
Doubly Linked List is the node has two pointers which link to previous and next one. It is useful to traverse back and forth.
Here is some example using doubly linked list
- Music player
- Undo-Redo functionality
 Circular Linked List
Circular Linked List
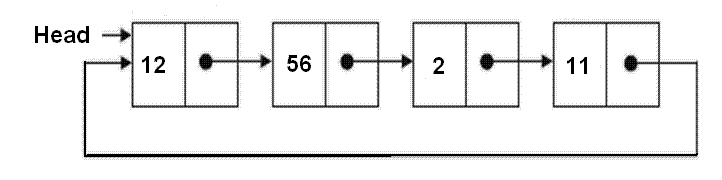
- https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/circular-linked-list-set-2-traversal/
Skip List
Skip List is multiple level list. The problem of linked list is that traversing is taking time O(n). Skip List allows us to skip unnecessary nodes to traverse which makes searching faster than regular linked list.
Implementation
https://github.com/ceejbot/skiplist
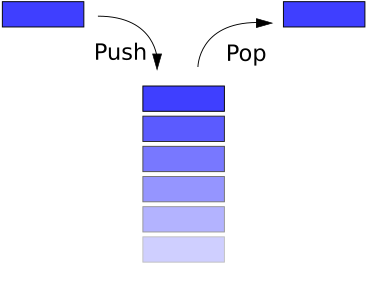
Stack
Unlike Linked List and Array, Stack & Queue is structure to determining how elements are inserted and deleted. Stack and Queue is implemented with either Array or Linked List.
When to use
Queue is FILO (First In Last Out) data structure. It is used for storing data in FILO order. Pop and Shift are O(1) and searching and access is O(n).
Example
Browser History
Call Stack (Function call) on browser
Type
Queue
When to use
Queue is LILO (Last In Last Out) data structure. It is used for storing data in LILO order. Enqueue and Dequeue are O(1) and searching and access is O(n).
Example
- Message queue on event loop (https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/JavaScript/EventLoop\
- LRU Cache
Type
- Queue
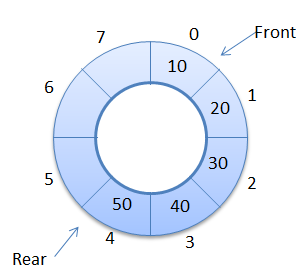
- Circular queue (https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Circular_buffer\
- Priority queue (https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=wptevk0bshY\
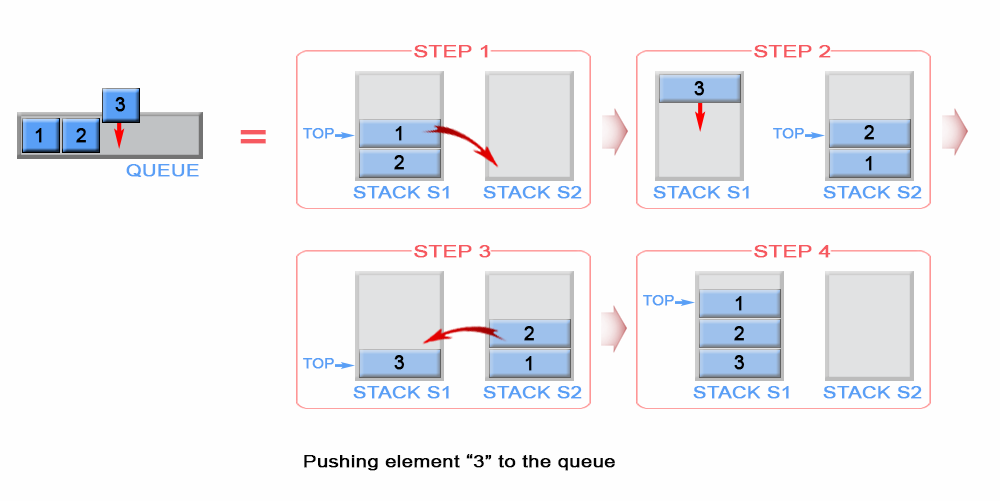
- Queue with 2 stacks
Queue

Circular queue
Priority queue
Queue with two stacks
https://stackoverflow.com/questions/2050120/why-use-two-stacks-to-make-a-queue
Tree
It makes easy to do data Indexing, and search.
Example
Directory Tree, Domain Tree, Syntax Tree, DOM Tree
https://reactjs.org/docs/reconciliation.html
Type
Binary Tree
Binary search tree
Heap
Self Balanced binary tree
AVL tree
red-black tree
splay tree
2–3 tree
N-ary tree
- B-Tree
- Trie
Binary Search Tree (Imbalanced)

Common Property
| value | contains value itself |
|---|---|
| left | contains left child |
| right | contains right child |
Common Operation
| Operation | Time Complexity | Space Complexity | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Add Node | Add Node to the end of node | O() | |
| Delete Node | Delete Node and re-connectits child and parent if it is needed | O(1) | |
| Get max | Get Maximum number of the tree | O(logN) | |
| Get min | Get minimum number of tree | O(logN) | |
| Max Height | Calculate Max Height of the tree | O(N) | |
| isBalanced | Check if the tree is balanced or not. The difference of the height of tree should be 1. If it is more than 1, it is not balanced. | O(N) | |
| Breath First Search | Search nodes from the closest nodes | O(N) | |
| Depth First Search | Search nodes from the deepest nodes | O(N) | |
| Merge two tree | |||
| Reverse Tree |
Self Balancing Binary Tree
The problem of imbalanced binary tree is that it could be Linked List-ish structure if data to be inserted is sorted already. Let's say if we insert 10, 9, 8, 7, 6, 5, 4, 3, 2, 1. It will be like Linked List because each elements will be inserted on left side. The time complexity of searching in this case is O(n) instead of O(log n). The more tree is balanced, the faster searching is.
- AVL Tree
- Red Black Tree
- Splay Tree
https://github.com/gwtw/js-data-structures
AVL tree
AVL tree is one of the self balancing trees. AVL tree keeps tree balanced by making sure the heights of two child subtree of any nodes differ by at most one. If the difference is over one, the tree will be restore elements by rotating elements.

Red Black Tree

Reference
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=qvZGUFHWChY
Splay Tree
Splay tree is suitable to access same element as you did before. It is used for cache and garbage collection implementation.
N-ary Tree
B-Tree
B-Tree is used to index databases
Reference
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=C_q5ccN84C8
https://github.com/kflu/btree.js/blob/master/lib/btree.js
2–3 tree
Trie
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=CX777rfuZtM
Tree Traversal
- Breath First Traversals
Breath First Traversals is the way to traverse tree from same level. Breath First Search can be implemented using queue data structure.
Depth First Traversals
- Inorder Traversal (Left-Root-Right)
- Preorder Traversal (Root-Left-Right)
- Postorder Traversal (Left-Right-Root)
https://stackoverflow.com/questions/33703019/breadth-first-traversal-of-a-tree-in-javascript
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=uWL6FJhq5fM
Exercise
https://www.hackerrank.com/domains/data-structures?filters[subdomains][]=trees
Advance
https://stackoverflow.com/questions/5894879/detect-differences-between-tree-structures
Heap
Heap is a special case of balanced binary tree data structure where the root-node key is compared with its children and arranged accordingly. Suppose we have [10, 20, 30, 40, 50], this array represents tree like below.
left = 2 * i + 1
right = 2 * i + 2
parent = (i - 1) / 2
If you access index 1, left node of index 1 is located index 3 and right is located at index 4.

Min-Heap
− Where the value of the root node is less than or equal to either of its children.

Max-Heap
− Where the value of the root node is greater than or equal to either of its children.

Heapify (The process building heap from array)
| Algorithm | Description | Time Complexity |
|---|---|---|
| siftDown | swaps a node that is too small with its largest child (thereby moving it down) until it is at least as large as both nodes below it. | O(n) |
| siftUp | swaps a node that is too large with its parent (thereby moving it up) until it is no larger than the node above it. | O(n * logN) |
Since siftDown is faster than shiftUp, siftDown is used to build valid heap. However, when it comes to insertion, time complexity of siftUp is O(logN) in the worst case, and O(1) in the best case (It is same behavior as inserting element in the array if order is already proper).
https://github.com/google/closure-library/blob/master/closure/goog/structs/heap.js#L52
https://stackoverflow.com/questions/9755721/how-can-building-a-heap-be-on-time-complexity
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=dM_JHpfFITs
Graph

Example
- Web
- Social Network
- Map (Routing)
https://www.quora.com/What-are-some-real-life-examples-of-Breadth-and-Depth-First-Search
Common Operation
- Adding an edge (node)
- Delete an edge
- Detect an edge
- Find a path between two veritcies
- Find a neighbor of a vertex
| Time Complexity | Space Complexity | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Add a node | Adding a node | ||
| Delete a node | Deleting a node | ||
| Add an edge | Adding a connection | ||
| Delete an edge | Deleting a connection | ||
| Find a node | Find an edge | ||
| Find a path between | |||
https://algs4.cs.princeton.edu/42digraph/
Type
Directed Graph
- Weighted Directed Graph
Undirected Graph
Words
| Vertex | Node |
|---|---|
| Edge | Connection |
| Directed Graph | A graph has direction information. For instance, map is directed graph because some streets are one way. |
| Undirected Graph | A graph has no direction information. For example, social network like Facebook because it is bi-directed. |
| DAG | Directed Acyclic Graph |
| Strongly Connected Component | Graph can be part. Directed Graph can be strongly connected if there is a path in each direction between each pair of vertices of the graph |
Connected Component
https://www.cs.usfca.edu/~galles/visualization/ConnectedComponent.html
Implementation
- Adjacency List
- Adjacency Matrix
https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/implementation-graph-javascript/
https://www.cs.usfca.edu/~galles/visualization/DFS.html
Common traversing and finding a path algorithm
Dijkstra's algorithm
Floyd Warshall algorithm
Bellman Ford algorithm
Karger's algorithm
Topological sort
Resource
https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/graph-and-its-representations/
http://tech-blog.abeja.asia/entry/2017/04/27/105613
https://classroom.udacity.com/courses/cs215
https://www.coursera.org/learn/advanced-data-structures
http://www.dais.is.tohoku.ac.jp/~shioura/teaching/ad09/ad09-09.pdf (JP)
Hash Table
https://hackernoon.com/data-structures-in-javascript-pt-2-hash-tables-8a6cc8ae3bd3
How you should approach the interview
- Articulate/code up a working solution \(even if it feels inefficient\) and then iterate rather than immediately trying to jump to the clever solution, if you cannot explain your solution clearly in 5 minutes, it's probably too complex for the problem at hand.
- Make sure you are asking clarifying questions as you go along \(there will not be tricks but you will need to ensure you have all the info you need\).
- Practice talking through your coding out loud while you are doing it - the interviewers need to see where you are headed with your solutions and if you talk they can provide hints.
- Spend a little time thinking about how you would walk someone else through your past projects, what you did on them \(as opposed to what your team did\), and what you learned from them.
- Come prepared with questions for your interviewer - this is just as much a chance for you to ensure that this is the place you want to be.
- Make sure you use good test cases that will find edge/corner cases. You will need to debug your code.
- Remember the interviewer will ask for a quick intro, please be prepared to talk about your most recent technical work quickly but in detail so it doesn't eat into your coding time.
You will need to demonstrate practical mastery of the following. -
Arrays and lists, binary trees, hash tables, stacks and queues, basic graph representations; an understanding of data structure fundamentals like pointers \(as if you weren't using an object oriented language\).
Make sure you have both time and space complexity down for the data structures you end up using in your solutions – become fluent in Big O Notation; knowing O\(n\), O\(1\), etc is important.
Also look over search through data structures -
understand how to implement iterators
understand binary search, and how hashes work, have your sorts down - merge, quick, bucket sorts,
know how to traverse a graph \(either BFS or DFS\)
understand how to do recursions.
You will need to write these out and explain them to another person on a white board so practice this!
trie
heap
set
red-black trees
randomized quicksort
dynamic programming
heap sort
radix sort
spanning tree
minimum cuts.
Ensure you use variable names that demonstrate to the READER that you know what you are talking about \(not just to you\). i.e. use 'nextPointer' vs 'abc', don't put data type \(like 'string' or 'int'\) in the name, use names that say what it is USED FOR not what it IS. Ask yourself: Would someone who has never spoken to you be able to understand what this variable is for?
Here is a graphic to summarize the above info:http://www.crackingthecodinginterview.com/uploads/6/5/2/8/6528028/handout_-_cracking_the_coding_skills.png
A Quora answer on how to prep for a technical interview:https://www.quora.com/How-do-I-prepare-for-a-software-engineering-job-interview
Business Insider Article, A Facebook developer shares 7 secrets to acing an engineering interview:http://www.businessinsider.com/how-to-prepare-for-facebook-engineering-interview-2016-3
Resource
https://mgechev.github.io/javascript-algorithms/index.html
https://github.com/duereg/js-algorithms/tree/master/lib
https://hackernoon.com/breadth-first-search-in-javascript-e655cd824fa4
https://towardsdatascience.com/the-5-clustering-algorithms-data-scientists-need-to-know-a36d136ef68